Medicaid Expansion Expands Access to Mental Health Care
Recent research from the National Bureau of Economic Research suggests that the Medicaid expansion under the Affordable Care Act increased access to mental health care.
Read Time: 1 minutes
Published:
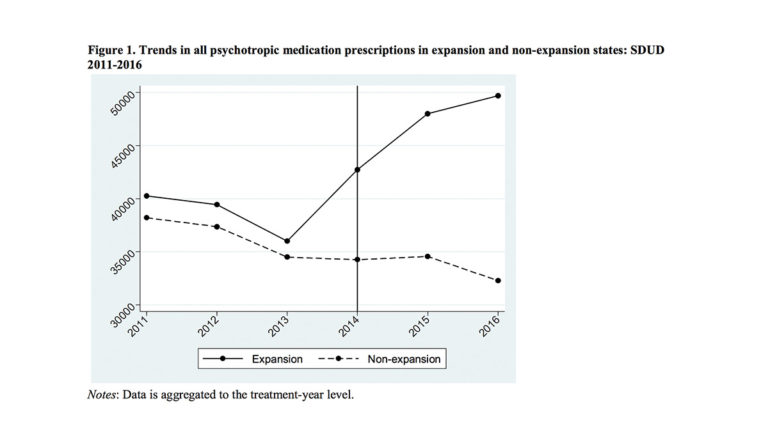
Recent research from the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) suggests that the Medicaid expansion under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) increased access to mental health care. Medicaid expansion states saw an increase of 22% in Medicaid-financed psychotropic prescriptions in comparison to non-expansion states. Psychotropic medications are recommended by the American Psychiatric Association to be part of treatment approach for most major mental illnesses.
This study does not show whether patients in Medicaid expansion states fill the prescriptions and adhere to the given treatment. However, the demonstrated increase in prescriptions suggests that “public insurance expansions allow low-income individuals with mental illnesses to access valuable healthcare services.” As the authors note, low income populations are typically at higher risk for mental illness and less likely to be insured. Thus, the Medicaid expansion directly benefits high risk groups that may not have had insurance coverage before.
Databyte via Johanna Catherine Maclean, Benjamin L. Cook, Nicholas Carson, and Michael F. Pesko, Public Insurance and Psychotropic Prescription Medications for Mental Illness. National Bureau of Economic Research.



